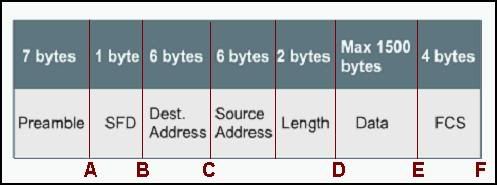
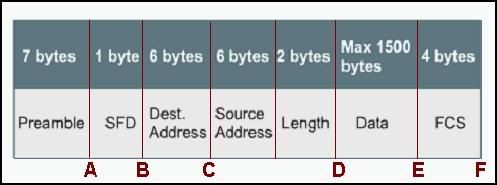
Take Assessment - Final Exam - CCNA 3 Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing (Version 3.1)
1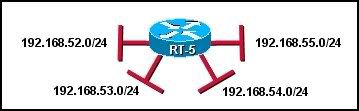
Refer to the graphic. What is the most efficient summarization of the routes attached to router RT-5?
• 192.168.0.0/16
• 192.168.52.0/24
• 192.168.48.0/22
• 192.168.52.0/22
• 192.168.51.0/23
• 192.168.48.0/21
2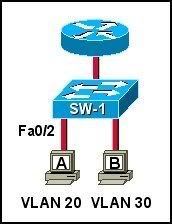
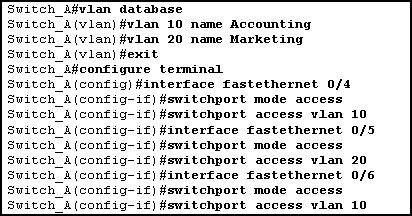
Refer to the exhibit. Which sequence of commands is required to configure switch port Fa0/2 for host A?
• SW-1(config)# interface vlan 20
SW-1(config-if)# switchport mode access 20
• SW-1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/2
SW-1(config-if)# switchport mode access
SW-1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 20
• SW-1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/2
SW-1(config-if)# vlan 20
• SW-1(config)# interface vlan 20
SW-1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
3 Which layer of the hierarchical three-layer design model combines traffic from multiple IDFs?
• access
• backbone
• distribution
• core
4 A network administrator is removing several VLANs from a switch. When the administrator enters the no vlan 1 command, an error is received. Why did this command generate an error?
• VLANs can only be deleted by the user who created them.
• VLAN 1 can not be deleted until another VLAN has been assigned its responsibilities.
• The command was not entered properly, which caused a syntax error to occur.
• VLAN 1 can not be deleted until all ports have been removed from it.
• VLAN 1 is the management VLAN by default and can not be deleted.
5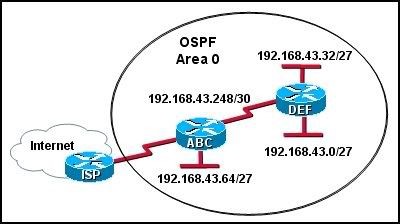
Refer to the exhibit. Which group of commands will correctly configure router ABC to use OSPF?
• ABC(config)# router ospf 99
ABC(config-router)# network 192.168.43.64 255.255.255.224 area 0
ABC(config-router)# network 192.168.43.248 255.255.255.248 area 0
• ABC(config)# router ospf 1
ABC(config-router)# network 192.168.43.64 0.0.0.31 area 0
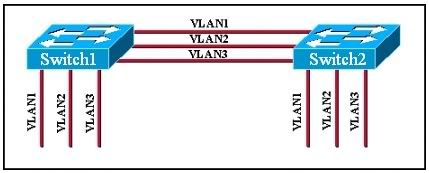
ABC(config-router)# network 192.168.43.248 0.0.0.3 area 0
• ABC(config)# router ospf 1
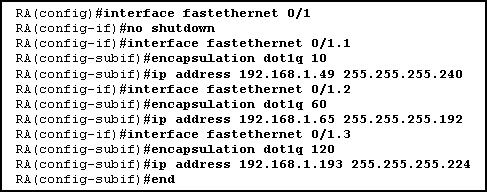
ABC(config-router)# network 192.168.43.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
ABC(config-router)# network 192.168.43.248 0.0.0.3 area 0
• ABC(config)# router ospf 0
ABC(config-router)# network 192.168.43.64 0.0.0.31 area 0
ABC(config-router)# network 192.168.43.248 0.0.0.3 area 0
6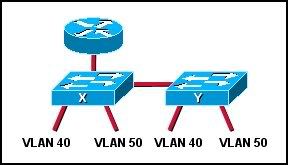
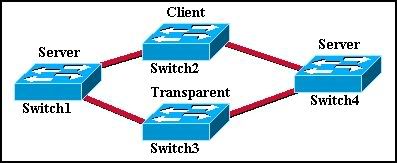
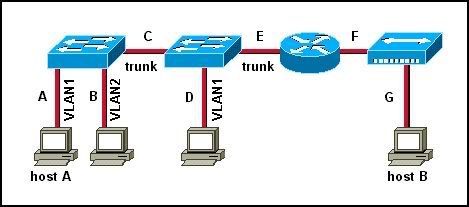
Refer to the exhibit. Two Catalyst switches are connected, and both switches have ports configured for VLANs 40 and 50 as shown. What will allow hosts on the same VLAN to communicate with one another across the different switches?
• trunking
• STP
• VTP
• routing
7 Which characteristics of RIPv1 are different from RIPv2? (Choose three.)
• its use of the hop count metric
• its use of broadcast updates
• its use of split horizon as a stability feature
• the authentication of updates
• its exclusively classful routing
• its hop count maximum of 15
8 Employees of XYZ Company connect their laptop computers to the office LAN using Ethernet ports. The Cisco switches used in the company network are configured with port security. At which layer of the three-layer design model do these switches operate?
• physical
• distribution
• data link
• access
• core
9 Which of the following tasks must be completed to configure a router interface to serve the newly added network 192.168.10.64/27 and to advertise this network over RIP v2? (Choose three.)
• RIP v2 must be configured with the network command and the IP network number for the new network.
• RIP v2 must be configured with the network command and the IP host address and subnet mask for the newly activated interface.
• The router must be configured with the ip subnet-zero command so that this network can be added and advertised.
• A network host address and subnet mask must be applied to the newly activated interface.
• The routing protocol must be activated with the router rip and version 2 commands.
• RIP v2 must be configured on the other enterprise routers with an entry for the newly added network.
10 Which two statements describe Spanning Tree Protocol? (Choose two.)
• It eliminates Layer 2 loops in network topologies.
• It eliminates the need for redundant physical paths in network topologies.
• It can only be used in networks in which Layer 2 switching is in use.
• It can only be used in networks where both routers and switches are used together.
• It can only be used in networks where routers are installed.
11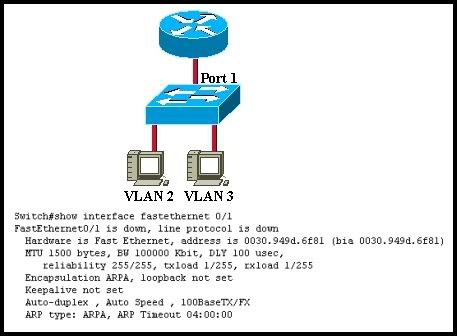
Refer to the graphic. The host on VLAN 2 cannot communicate with the host on VLAN 3. Which of the following could be the problem based on the output of the show interface fastethernet 0/1 command from the switch?
• The switch port 1 is not set to access mode.
• The router interface connected to switch port 1 is shut down.
• The router is not configured for trunking.
• The switch port is not configured for full duplex or a speed of 100 Mbps.
12 What is added to a bridge CAM table as a frame passes through a switch?
• source IP address
• destination IP address
• source MAC address
• destination MAC address
13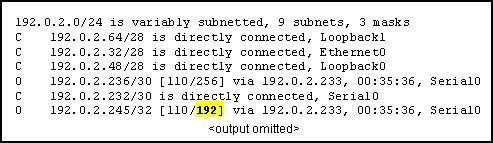
Refer to the routing table shown in the exhibit. What is the meaning of the highlighted value 192?
• It is the value assigned by the Dijkstra algorithm that designates the number of hops in the network.
• It is the value used by the DUAL algorithm to determine the bandwidth for the link.
• It is the metric, which is cost.
• It is the administrative distance.
14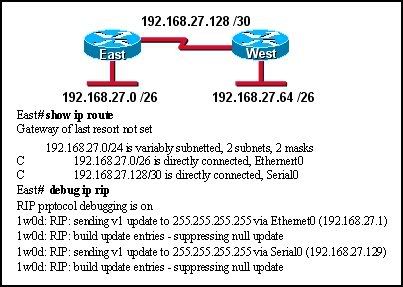
Refer to the exhibit. Routers East and West are configured using RIPv1. Both routers are sending updates about their directly connected routes. The East router can ping the West router serial interface and West can ping the serial interface of East. However, neither router has dynamically learned routes from the other. What is most likely the problem?
• A gateway of last resort is required.
• Subnetting is not supported by RIPv1.
• VLSM is not supported by RIPv1.
• One of the routers needs a clock rate on the serial interface.
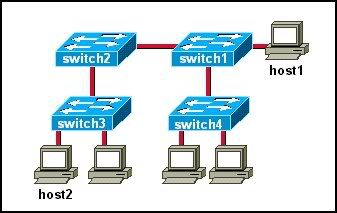
15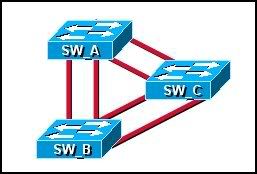
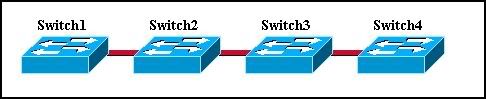
Refer to the exhibit. What is an advantage of this network design?
• It maximizes the number of ports available for hosts.
• It provides multiple paths for connectivity in the event of link failure.
• It provides multiple paths for Layer 2 broadcasts to circulate through the network.
• It allows Spanning Tree to forward traffic across redundant paths simultaneously.
16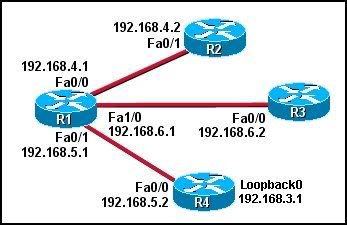
Refer to the exhibit. What will be the result of DR elections in the OSPF network shown? (Choose three.)
• R1 will be DR of the 192.168.4.0/24 network.
• R2 will be DR of the 192.168.4.0/24 network.
• R1 will be DR of the 192.168.5.0/24 network.
• R4 will be DR of the 192.168.5.0/24 network.
• R1 will be DR of the 192.168.6.0/24 network.
• R3 will be DR of the 192.168.6.0/24 network.
17 What are two advantages provided by OSPF authentication? (Choose two.)
• It ensures that routing information comes from a valid source router.
• It ensures that OSPF routing information takes priority over RIP or EIGRP updates.
• It encrypts routing tables to prevent unauthorized viewing.
• It reduces OSPF information exchange overhead.
• It prevents routing information from being falsified in transit.
18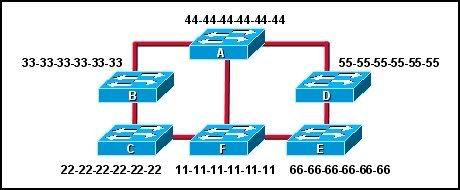
Refer to the exhibit. Each switch is shown with its MAC address. Which switch will be elected as the spanning-tree root bridge if the switches are configured with their default priority values?
• switch A
• switch B
• switch C
• switch D
• switch E
• switch F
19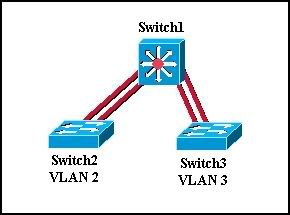
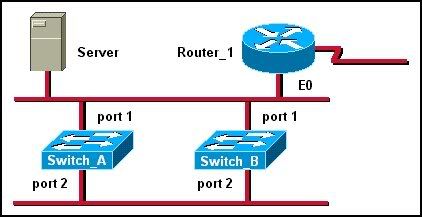
Refer to the graphic. Switch 2 has computers attached that belong to VLAN 2. Switch 3 has computers attached that belong to VLAN 3. Switch 1 is a Cisco 2926G Layer 3 switch that has a route module installed. Switch 1 provides connectivity to the other switches and is used to route between the VLANs. At which layer of the three-layer switch design model does Switch 1 operate?
• physical
• data link
• core
• access
• network
• distribution
20 A network administrator is having problems with excessive collisions on the corporate network. If the network currently uses hubs, what is the most cost effective way to reduce collisions?
• add additional hubs
• replace hubs with switches
• replace hubs with access points
• add a router to every hub segment
21 Which statements describe features of full-duplex Ethernet? (Choose three.)
• allows packets to be received and sent simultaneously by a host
• requires a minimum of two wires
• reduces the number of collisions
• allocates between 60 and 80 percent of available bandwidth in both directions
• allocates 100 percent of the bandwidth in both directions
• increases the number of broadcast domains
22 What does a constant green SYSTEM LED indicate on a Catalyst switch?
• The switch has passed POST and is working properly
• The switch has failed POST.
• The switch is in the process of initializing ports.
• The switch is going through POST.
• The switch is actively sending and receiving frames.
23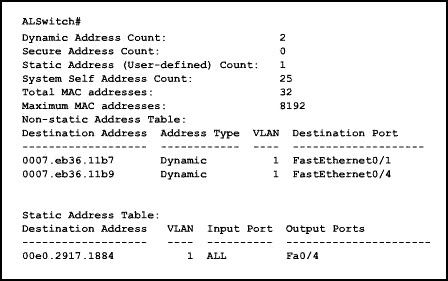
Refer to the exhibit. Which command will remove the static address from the MAC address table?
• ALSwitch(config)# no mac-address-table entry 00e0.2917.1884 fastethernet interface 0/4 VLAN 1
• ALSwitch(config)# no mac-address-table entry 00e0.2917.1884 VLAN 1 fastethernet 04
• ALSwitch(config-if)# no mac-address-table entry static 00e0.2917.1884 VLAN 1 fastethernet 04
• ALSwitch(config-if)# no mac-address-table static 00e0.2917.1884 VLAN 1 fastethernet 04
• ALSwitch(config)# no mac-address-table static 00e0.2917.1884 interface fastethernet 0/4 VLAN 1
24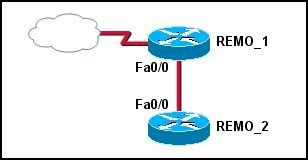
Refer to the OSPF network in the exhibit. Router REMO_2 has been elected DR, but router REMO_1 is the more powerful router. How can the network administrator configure REMO_1 to force it to be elected as DR?
• REMO_1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
REMO_1(config-if)# ospf priority 0
• REMO_1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
REMO_1(config-if)# ip ospf priority 0
• REMO_1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
REMO_1(config-if)# ip ospf priority 255
• REMO_1(config)# ospf priority 1
• REMO_1(config)# ip ospf priority 255
25 What is the first step in the spanning-tree process?
• elect a designated switch
• use a router to locate a default gateway
• elect a root bridge
• determine the path cost of each active port on the switch
26 Which of the following statements is true when VTP is configured on a switched network that incorporates VLANs?
• VTP is only compatible with the 802.1Q standard.
• VTP adds to the complexity of managing a switched network.
• All VTP hello packets are routed through VLAN 1 interfaces.
• Changes made to the network can be communicated to all switches dynamically.
27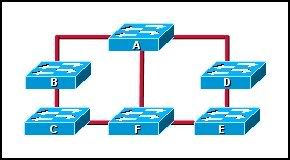
Refer to the graphic. The network has converged. Network traffic analysis indicates that switch A should be the STP root bridge. However, switch F has been elected root bridge of the STP tree. The switches are all set to the default spanning-tree bridge priority value. How can the network administrator change the root bridge to switch A?
• Configure the bridge priority of switch A to a 1.
• Configure the bridge priority of switch A to a 65,565.
• Configure the bridge priority of switch F to 255.
• Configure the bridge priority of switch F to 32,768.
28 Which of the following statements are true about routers that are running EIGRP? (Choose three.)
• They can support multiple routed protocols.
• They can support only link-state protocols.
• They send their entire routing tables to neighboring routers.
• They send partial routing updates in response to topology changes.
• They send routing updates to all other routers in the network.
• They use hello packets to inform neighboring routers of their status.
29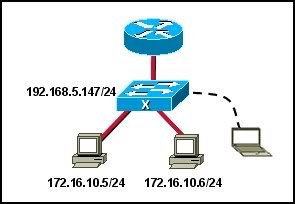
Refer to the exhibit. A company always uses the last valid IP address in a subnetwork as the IP address of the router LAN interface. A network administrator is using a laptop to configure switch X with a default gateway. Assuming that the switch IP address is 192.168.5.147/24, what command will the administrator use to assign a default gateway to the switch?
• X(config)# ip default-gateway 192.168.5.254
• X(config)# ip gateway 192.168.5.1
• X(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.5.1
• X(config)# ip default-route 192.168.5.1
• X(config)# ip route 192.168.5.254 255.255.255.0 fastethernet 0/0
30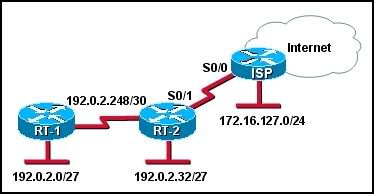
Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration commands will direct outbound traffic from RT-2 to the ISP and inbound traffic from the ISP to network 192.0.2.0/27?
• RT-2(config)# ip route 172.16.127.0 255.255.255.0 serial 0/1
ISP(config)# ip route 192.0.2.0 255.255.255.224 serial 0/0
• RT-2(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/1
ISP(config)# ip route 192.0.2.0 255.255.255.224 serial 0/0
• RT-2(config)# ip route 172.16.127.0 255.255.255.0 serial 0/1
ISP(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/0
• RT-2(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/1
ISP(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/1
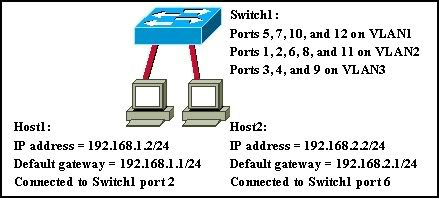
31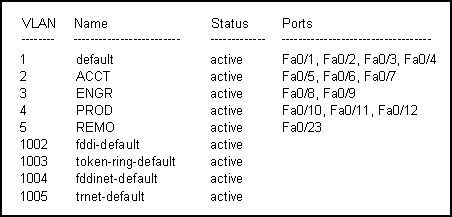
Refer to the output in the exhibit. What is true about the configuration of this switch?
• Three ports have been assigned to the management VLAN.
• VTP has been enabled for all ports.
• ARP requests issued by the host on port Fa0/12 will be seen by all hosts on the PROD VLAN.
• Hosts in the ACCT and ENGR VLANs must have IP addresses in the same subnet in order to exchange data between VLANs.
32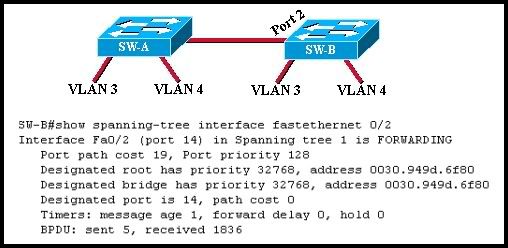
Refer to the graphic. What is the first parameter used to determine which switch is selected as the root bridge in the spanning-tree process?
• highest Layer 2 address
• highest priority number
• highest path cost
• lowest Layer 2 address
• lowest priority number
• lowest path cost
33 When should EIGRP automatic summarization be turned off?
• when a router has not discovered a neighbor within three minutes
• when a router has more than three active interfaces
• when a router has discontiguous networks attached
• when a router has less than five active interfaces
34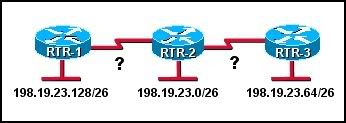
Refer to the exhibit. If the network is running RIP v2, which subnetworks can be assigned to the serial links between RTR-2 and the two other routers?
• 198.19.23.192/30 and 198.19.23.196/30
• 198.19.23.160/30 and 198.19.23.164/30
• 198.19.23.96/30 and 198.19.23.100/30
• 198.19.23.32/30 and 198.19.23.160/30
• 198.19.23.4/30 and 198.19.23.8/30
35 Which switching method increases latency and reliability more than any other method?
• cut-through
• fast-forward
• fragment-free
• store-and-forward
36 What are two advantages of adding switches to a network that has no VLANs configured? (Choose two.)
• Switches help eliminate collision domains.
• Switches create permanent virtual communication circuits.
• Switches allow bandwidth to be fully utilized.
• Switches decrease network throughput.
• Switches shrink the size of broadcast domains.
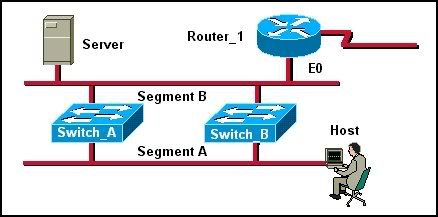
37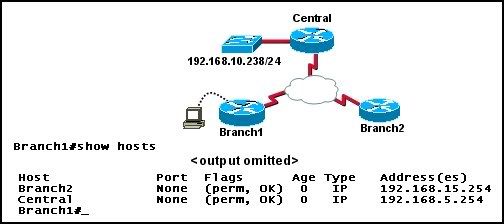
Refer to the network and command output shown in the exhibit. A network administrator located at the Branch1 site needs to check the configuration of a switch located at the Central office. Which command can be used to gain remote access to the Central LAN switch, assuming the switch is assigned the IP address 192.168.10.238/24?
• Branch1# dial Central 192.168.10.238
• Branch1(config)# line vty 0 4
Branch1(config-line)# telnet
• Branch1# telnet Central
• Branch1# telnet 192.168.10.238
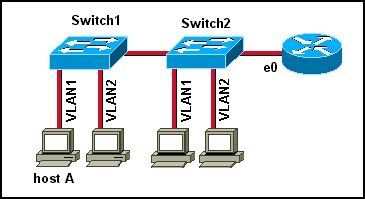
38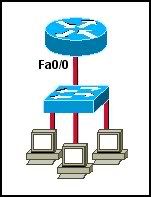
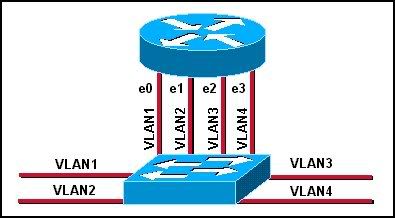
Refer to the exhibit. Assuming that VLANs are not configured on the switch, how many broadcast domains are there?
• one
• two
• three
• four
• five
• six
39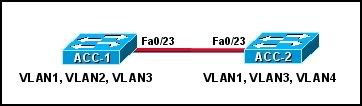
Refer to the exhibit. How should an administrator configure the ports on switches ACC-1 and ACC-2 to allow hosts on the same VLAN to communicate across the two switches?
• as trunks
• as access ports
• as channels
• as inter-VLAN ports
• as bridge ports
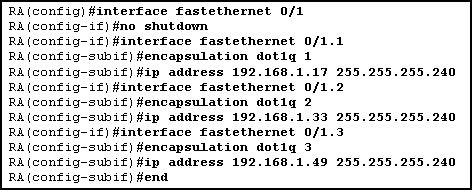
40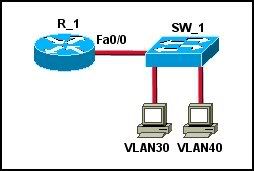
Refer to the exhibit. Which set of commands should be used on the router to provide communication between the two hosts connected to the switch?
• R_1(config)# interface vlan 30
R_1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk dot1q
R_1(config-if)# interface vlan 40
R_1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk dot1q
• R_1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
R_1(config-if)# mode trunk dot1q 30 40
R_1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
• R_1(config)# interface vlan 30
R_1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0
R_1(config-if)# no shutdown
R_1(config-if)# interface vlan 40
R_1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.40.1 255.255.255.0
R_1(config-if)# no shutdown
• R_1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
R_1(config-if)# no shutdown
R_1(config-if)# interface fastethernet 0/0.3
R_1(config-if)# encapsulation dot1q 30
R_1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0
R_1(config-if)# interface fastethernet 0/0.4
R_1(config-if)# encapsulation dot1q 40
R_1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.40.1 255.255.255.0
41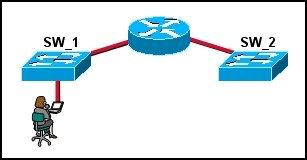
The network administrator shown in the exhibit is connected to an Ethernet LAN port on SW_1. The administrator needs to verify the configuration of the newly installed switch SW_2. What must be done so that the administrator can access SW_2 with a web browser? (Choose three.)
• Set the password on the management VLAN.
• Establish connectivity of the host to SW_2.
• Configure IP addressing parameters on SW_2.
• Configure the hostname on SW_2.
• Activate the HTTP service on SW_2.
42 How do EIGRP routers establish and maintain neighbor relationships?
• by exchanging neighbor tables with directly attached routers
• by comparing known routes to information received in updates
• by exchanging of hello packets with neighboring routers
• by dynamically learning new routes from neighbors
• by exchanging routing tables with directly attached routers
43 What are three attributes of distance vector routing protocols? (Choose three.)
• Hello packets are used to form neighbor adjacencies.
• Each router sends its entire routing table in routing updates.
• Periodic updates are sent to neighboring routers.
• Distance vector protocols converge more rapidly than link-state protocols do.
• Because of their frequent periodic updates, distance vector protocols after convergence use more bandwidth than link-state protocols do.
• Distance vector protocols are less prone to routing loops than are link-state protocols.
44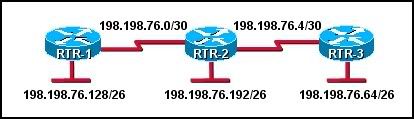
Refer to the exhibit. Routers RT-1 and RT-3 are completely configured. The administrator needs to configure the routing protocol on router RTR-2 so that communication occurs throughout the network. Which group of commands will successfully configure EIGRP on RTR-2?
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.0
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.0 0.0.0.3 no-summary
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.4 0.0.0.3 no-summary
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.128 0.0.0.192 no-summary
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.128 0.0.0.63 area 0
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.0 0.0.0.3
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.4 0.0.0.3
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.128 0.0.0.192
45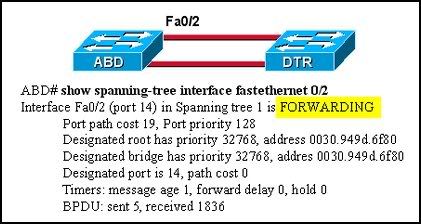
Refer to the exhibit. What does "FORWARDING" mean in the command output shown?
• The switch is receiving BPDUs, but not sending data frames.
• The switch is participating in an election process by forwarding the BPDUs it receives.
• The switch is sending and receiving data frames.
• The switch is receiving BPDUs and populating the MAC address table, but not sending data.
46 The following command was added to a router configuration:
ip route 198.19.150.0 255.255.255.0 192.0.2.249
What two effects will this command have? (Choose two.)
• It will create a static route to the 198.19.150.0/24 network.
• It will create a default route using the interface with the IP address 192.0.2.249 as the next hop.
• All packets with an unknown destination address will be forwarded to the 198.19.150.0/24 network.
• Information about the 198.19.150.0 network learned dynamically will be ignored as long as this configuration command is in effect.
• The route will be marked with an "R" in the routing table.